- PATIENT FORMS | REQUEST A CONSULTATION | CONTACT US
- 1-844-NSPC-DOC
Aneurysms of the Brain
What Is a Brain Aneurysm?
Take ActionBrain Aneurysm Causes
A condition as complicated as a brain aneurysm has a variety of causes and risk factors associated with it.
These contributing factors can be managed through proper treatment and behavior; discuss this with your physician:
- Hypertension—Those who suffer from high blood pressure run a greater risk of developing a brain aneurysm.
- Smoking—Smoking is not only a contributing factor and direct cause of hypertension, but it can also aggravate aneurysms and result in bleeding in the fluid-filled space around the brain.
- Obesity—People who suffer from obesity often have high cholesterol levels and suffer from atherosclerosis, which is a hardening of the arteries and another risk factor for aneurysms.
- Balance problems
- Numbness or paralysis of your face
Other risk factors cannot be controlled, such as family history and genetic predisposition or diseases such as polycystic kidney disease or arteriovenous malformations. A family history of cerebral aneurysm is one of the leading indicators of whether a person may themselves develop one; this condition is unfortunately genetically heritable.
Brain Aneurysm Diagnosis
This condition can be diagnosed using one of these four methods:
- Computer Tomography – Often referred to as a CT scan, this diagnostic procedure can help to identify areas in the brain that may be bleeding. A lumbar puncture is sometimes used in conjunction with this scan if your physician suspects possible subarachnoid bleeding.
- Computed Tomography Angiogram – A CTA is a more powerful and precise version of the basic CT scan technology. It employs regular CT scanning along with additional computerized modeling techniques, and a special radioactive dye injected into the patient to help fully identify blood flow patterns.
- Magnetic Resonance Angiograph – An MRA uses magnetic fields and radio waves to produce results similar to those from a CT scan. A contrast material dye will often be used in order to help improve the quality of the medical imaging.
- Cerebral Angiogram – This is an x-ray based test that requires a catheter to be inserted in your groin or arm area, and then travel up through a blood vessel to your brain. This is the preferred method to diagnose very small brain aneurysms.
Brain Aneurysm Symptoms
The important thing to remember is that if you believe you are experiencing brain aneurysm symptoms, you should contact emergency services right away. If you are indeed experiencing a stroke or other major medical event, the faster you are able to begin receiving medical care, the better your long-term prognosis and the lower the chance that you will suffer brain damage. That said, keep in mind that often there will be no observable brain aneurysm symptoms until an event actually occurs; in fact, most of the time potential problems are discovered during the investigation and treatment of another, unrelated medical issue.
When an event does occur, however, a person may experience one or more of the following common symptoms:
- Headaches – The headaches associated with an aneurysm are extremely painful, and will be unlike other headaches a person may have experienced in the past.
- Acute Neck Pain – A sharp, acute neck pain may also be indicative that a major event is about to or is in the process of striking the patient
- Extreme Nausea/Repeated Vomiting – In many cases, patients will experience a feeling of extreme nausea, and may vomit repeatedly
- Blurred Vision Or Extreme Sensitivity To Light – Patients will often experience blurred or distorted vision, and light may cause them extremely painful headaches.
- Changes To Speech Patterns – A person may lose control over their speech when suffering an aneurysm or stroke; this is one of the most obvious signs.
- Fainting Spells/Loss Of Consciousness – Increased pressure inside the skull can result in a person experiencing fainting spells or loss of consciousness.
- Seizures – Sudden seizures in a person with no history of epilepsy or other neurological conditions is another major sign that they have possibly suffered a stroke or aneurysm.
If you or someone you know displays brain aneurysm symptoms, contact emergency services right away.
Aneurysms of the Brain Treatments
Your physician will consider a multitude of different factors when deciding on your particular treatment. They will evaluate your age and general health, the size and severity of the aneurysm, and any other pertinent risk factors. In general, brain aneurysm treatment breaks down into one of three basic courses of action:
Coil Embolization
In this brain aneurysm treatment, a tiny tube is inserted into the artery very close to the site of the aneurysm itself. A small coil made of metal is then inserted into the artery to reinforce it and relieve pressure in the area. Coil embolization is considered the less invasive of the two cerebrovascular neurosurgery treatment options.
Observation
Small aneurysms do not often rupture, so if yours is sufficiently small, the doctor may simply recommend long-term observation, as brain surgery can often prove risky even for patients in the best of health. Your physician will clearly explain the risk factors associated with choosing to wait and see, and you may require ongoing monitoring over the long term in this case.
Surgical Clipping
The third form of common brain aneurysm treatment is referred to as surgical clipping. A small clip is placed around the site of the aneurysm in an attempt to completely isolate it from blood flow, which significantly reduces the risk of it bursting. However, surgical clipping is not suitable for use 100% of the time; discuss the different cerebrovascular neurosurgery treatment options with your surgeon.
If you suffer from a brain aneurysm, our expert neurosurgeons will work closely with you to discuss all of your possible risk factors, as well as which treatment option is the best choice given your personal circumstance.
In the New York area—including Long Island offices—you can get world-class brain aneurysm treatments from the superb board-certified neurosurgeons at NSPC.

Related NSPC Center
Long Island Brain and Spine Tumor Center
NSPC provides state-of-the-art treatment of benign and malignant brain and spine tumors, using minimally invasive procedures like Gamma Knife®, Novalis TX™, and CyberKnife® rather than major surgery whenever appropriate. Our physicians also perform experienced pediatric neurosurgery — they give personalized, individual attention combined with knowledge and experience to take on the most challenging of cases.
Physicians
Connect With Our 7 Convenient Locations
across Long Island, NY
Our expert physicians, surgeons and doctors are ready to serve you at our 7 convenient locations across Long Island, NY. Connect today to learn how our award winning, world class experts can help.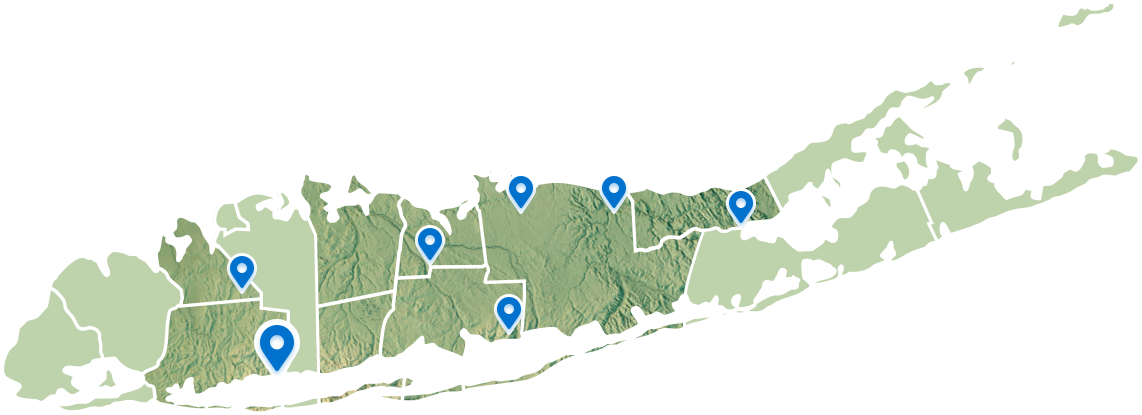
4250 Hempstead Turnpike Suite 4,
Bethpage, NY 11714
(516) 605-2720
COMMACK
353 Veterans Memorial Hwy,
Commack, NY 11725
(631) 864-3900
One Hollow Lane, Suite 212
Lake Success, NY 11042
(516) 442-2250
MANHATTAN
215 E. 77th Street Ground Floor
New York, NY 10075
(646) 809-4719
PORT JEFFERSON STATION
1500-8A Route 112,
Port Jefferson Station, NY 11776
(631) 828-3001
100 Merrick Road, Suite 128W
Rockville Centre, NY 11570
(516) 255-9031
WEST ISLIP
500 Montauk Hwy
West Islip, NY 11795
(631) 983-8400
World
Class
Expertise
For over 50 years & 350,000 patients NSPC has been a trusted global medical leader.
Contact us today for an appointment or consultation.
