- PATIENT FORMS | REQUEST A CONSULTATION | CONTACT US
- 1-844-NSPC-DOC
Resection of Cerebral Arteriovenous Malformation
What Is Resection of Cerebral Arteriovenous Malformation?
Cerebral arteriovenous malformations (AVMs) are abnormal tangles of blood vessels of the brain. A resection is the surgical removal of small AVMs that are on or near the surface of the brain.
As a treatment for cerebral AVMs, a microsurgical resection sometimes is part of a complementary procedure with stereotactic radiotherapy or used in coordination with embolization. Radiotherapy uses radiation doses to cause the lesions to clot and, over time, to close off. Embolization is an endovascular procedure where a catheter threaded up through the groin artery to the brain AVM delivers a material (such as a medical glue or a soft, metal coil) to block blood from supplying the AVM; however, the AVM remains. Thus, sometimes endovascular embolization may be performed before the resection.
What Happens During a Resection of Cerebral Arteriovenous Malformation Procedure?
A variety of factors such as the history of previous ruptures, the location of the AVM, the size and the presence of an aneurysm are reviewed to determine if a patient is a good candidate for a microsurgical resection of a cerebral arteriovenous malformation.
During the surgery, the patient is anesthetized and the head secured.
- A portion of the scalp is shaved.
- The surgeon performs a craniotomy (surgically opens the skull). After the skull is opened up, the dura (membrane covering the brain) is incised.
- The AVM is isolated from the neighboring brain tissue.
- The vessels providing blood to the AVM are clamped off.
- With microsurgical instruments, the AVM is resected (removed) from the tissue.
- Temporary drains may be installed to stop fluid build-up in the skull.
- The skull flap is put back in place and affixed with plates and small metal screws.
- Skin is put back and secured with sutures or surgical staples.
Recovery generally begins with one day in the intensive care unit and another four to six days in the hospital.
Connect With Our 7 Convenient Locations
across Long Island, NY
Our expert physicians, surgeons and doctors are ready to serve you at our 7 convenient locations across Long Island, NY. Connect today to learn how our award winning, world class experts can help.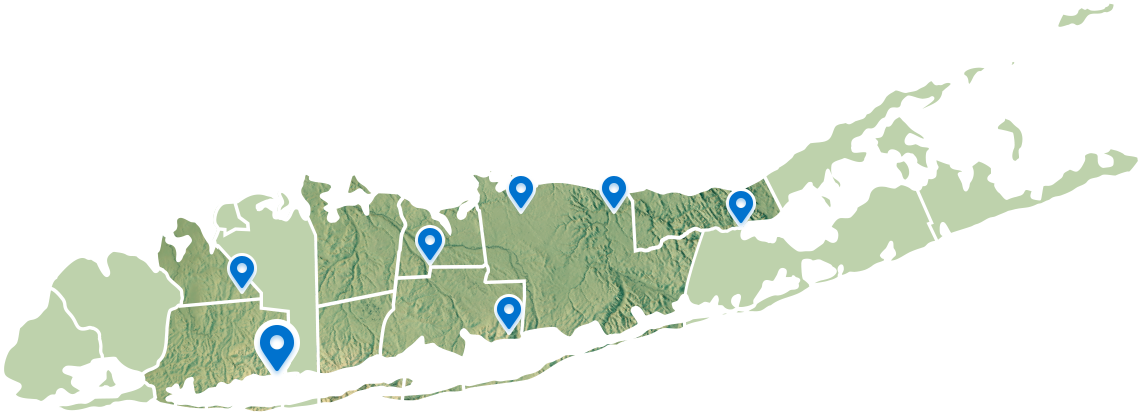
4250 Hempstead Turnpike Suite 4,
Bethpage, NY 11714
(516) 605-2720
COMMACK
353 Veterans Memorial Hwy,
Commack, NY 11725
(631) 864-3900
One Hollow Lane, Suite 212
Lake Success, NY 11042
(516) 442-2250
MANHATTAN
215 E. 77th Street Ground Floor
New York, NY 10075
(646) 809-4719
EAST SETAUKET
226 North Belle Mead Road, Suite C
East Setauket, NY 11733
(631) 828-3001
100 Merrick Road, Suite 128W
Rockville Centre, NY 11570
(516) 255-9031
WEST ISLIP
500 Montauk Hwy
West Islip, NY 11795
(631) 983-8400
World
Class
Expertise
For over 50 years & 350,000 patients NSPC has been a trusted global medical leader.
Contact us today for an appointment or consultation.